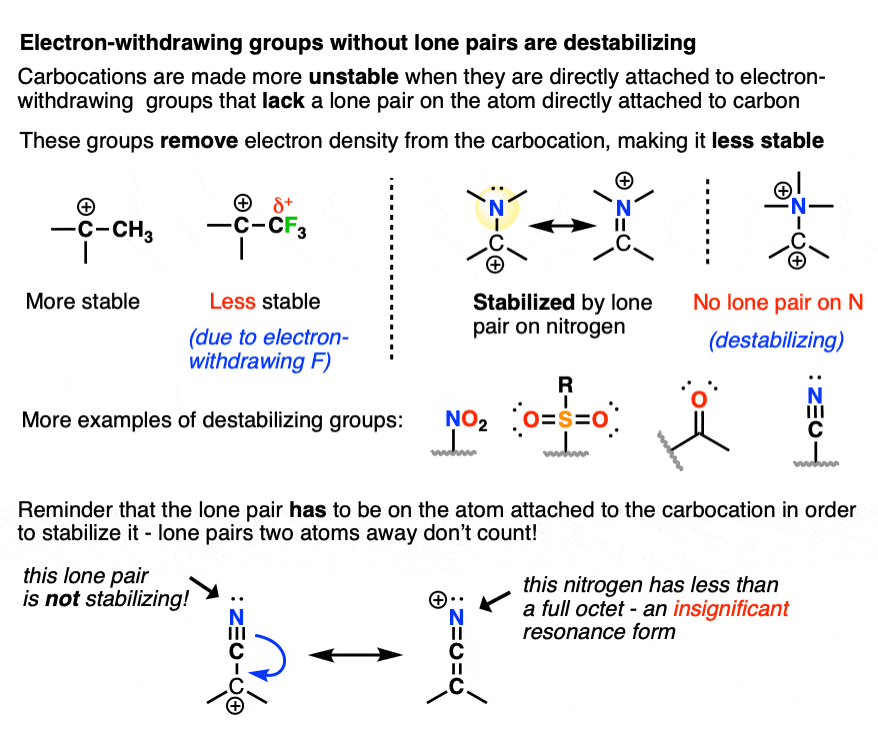
Carbocation Stability Rules . Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. describe the geometry of a given carbocation. describe the geometry of a given carbocation. Explain the relative stability of. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. to understand why markovnikov’s rule works, we need to learn more about the structure and stability of carbocations and about the. imagine a tightrope walker (a carbocation) trying to maintain balance. the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as the number of potential resonance forms increases. a carbanion is a nucleophile that determines stability and reactivity by several factors:
from www.masterorganicchemistry.com
Explain the relative stability of. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. describe the geometry of a given carbocation. to understand why markovnikov’s rule works, we need to learn more about the structure and stability of carbocations and about the. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. a carbanion is a nucleophile that determines stability and reactivity by several factors: the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as the number of potential resonance forms increases. imagine a tightrope walker (a carbocation) trying to maintain balance. describe the geometry of a given carbocation.
3 Factors That Stabilize Carbocations
Carbocation Stability Rules Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. describe the geometry of a given carbocation. a carbanion is a nucleophile that determines stability and reactivity by several factors: Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. describe the geometry of a given carbocation. Explain the relative stability of. imagine a tightrope walker (a carbocation) trying to maintain balance. to understand why markovnikov’s rule works, we need to learn more about the structure and stability of carbocations and about the. the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as the number of potential resonance forms increases.
From www.masterorganicchemistry.com
3 Factors That Stabilize Carbocations Carbocation Stability Rules describe the geometry of a given carbocation. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. imagine a tightrope walker (a carbocation) trying to maintain balance. the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as the number of potential resonance forms increases. Arrange a given series of carbocations in. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.youtube.com
Carbocations 2 Stability YouTube Carbocation Stability Rules Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as the number of potential resonance forms increases. Explain the relative stability of. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. describe the geometry of a given carbocation.. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.organicchemistrytutor.com
Carbocations Stability and Rearrangements — Organic Chemistry Tutor Carbocation Stability Rules Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as the number of potential resonance forms increases. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur.. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.bartleby.com
Arrange these carbocations in order of increasing stability. (a) (b) (c) bartleby Carbocation Stability Rules Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. imagine a tightrope walker (a carbocation) trying to maintain balance. Explain the relative stability of. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. to understand why markovnikov’s rule works, we need to learn more about the. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.masterorganicchemistry.com
3 Factors That Stabilize Carbocations Carbocation Stability Rules describe the geometry of a given carbocation. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. to understand why markovnikov’s rule works, we need to learn more about the structure and stability of carbocations and about the. a carbanion is a nucleophile that determines stability and reactivity by several factors: the stability. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.masterorganicchemistry.com
3 Factors That Stabilize Carbocations Carbocation Stability Rules Explain the relative stability of. to understand why markovnikov’s rule works, we need to learn more about the structure and stability of carbocations and about the. a carbanion is a nucleophile that determines stability and reactivity by several factors: describe the geometry of a given carbocation. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.masterorganicchemistry.com
3 Factors That Stabilize Carbocations Carbocation Stability Rules Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. describe the geometry of a given carbocation. to understand why markovnikov’s rule works, we need to learn more about the structure and stability of carbocations and about the. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. Carbocations are stabilized when. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.pinterest.com
Carbocation Stability Primary Secondary Tertiary Allylic and Benzylic Organic chemistry, Mcat Carbocation Stability Rules Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. describe the geometry of a given carbocation. Explain the relative stability of. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. imagine a tightrope walker (a carbocation) trying to maintain balance. describe the geometry of a. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.masterorganicchemistry.com
3 Factors That Stabilize Carbocations Carbocation Stability Rules Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. a carbanion is a nucleophile that determines stability and reactivity by several factors: imagine a tightrope walker (a carbocation) trying to maintain balance. describe the geometry of a given carbocation. the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From chemistry2134.blogspot.com
Carbocations Factors affecting their Stability Carbocation Stability Rules the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as the number of potential resonance forms increases. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. imagine a tightrope walker (a carbocation) trying to maintain balance. to. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.organicchemistrytutor.com
SN1 Reactions with Carbocation Rearrangements — Organic Chemistry Tutor Carbocation Stability Rules describe the geometry of a given carbocation. Explain the relative stability of. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. a carbanion is a nucleophile that determines stability and reactivity by several factors: Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. the stability. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From collegedunia.com
The order of stability of the following carbocations a) III>II> I b) II>III>I c) I>II>III d) III Carbocation Stability Rules Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. Explain the relative stability of. imagine a tightrope walker (a carbocation) trying to maintain balance. to understand why markovnikov’s rule works, we need to learn more about the structure and stability of carbocations and about the. a carbanion is a nucleophile that determines stability. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.clutchprep.com
Rank the following carbocations in order of decreasing stability Organic Chemistry Video Carbocation Stability Rules the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as the number of potential resonance forms increases. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. Explain the relative stability of. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From socratic.org
What stabilizes carbocation? Socratic Carbocation Stability Rules describe the geometry of a given carbocation. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. to understand why markovnikov’s rule works, we need to learn more about the structure and stability of carbocations and about the. describe the geometry of a given carbocation. Explain the relative stability of.. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.youtube.com
Carbocation Stability YouTube Carbocation Stability Rules Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. describe the geometry of a given carbocation. the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as the number of potential resonance forms increases. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.masterorganicchemistry.com
3 Factors That Stabilize Carbocations Carbocation Stability Rules a carbanion is a nucleophile that determines stability and reactivity by several factors: describe the geometry of a given carbocation. to understand why markovnikov’s rule works, we need to learn more about the structure and stability of carbocations and about the. the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as the number of potential resonance forms. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From trickychemistrysuman.blogspot.com
Stability of carbocation a detailed explanation DPO Udham Singh Nagar Carbocation Stability Rules a carbanion is a nucleophile that determines stability and reactivity by several factors: describe the geometry of a given carbocation. Explain the relative stability of. imagine a tightrope walker (a carbocation) trying to maintain balance. Carbocations are stabilized when they are adjacent to elements with electron pairs like oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Arrange a given series of. Carbocation Stability Rules.
From www.doubtnut.com
Taking into account the stability of various cycloalkanes and carbocat Carbocation Stability Rules imagine a tightrope walker (a carbocation) trying to maintain balance. Explain the relative stability of. Arrange a given series of carbocations in order of increasing or decreasing stability. a carbanion is a nucleophile that determines stability and reactivity by several factors: the stability of the carbocation tends to increase as the number of potential resonance forms increases.. Carbocation Stability Rules.